About Scaffolding
About Scaffolding
by Nick Gromicko
Scaffolds are temporary, elevated platforms with supporting structures that are used to support workers and their materials at construction sites. As defective scaffolds put workers at great risk, these structures should be inspected before each work shift, as well as after any event that may have caused damage.
Facts and Figures
According to a national study:
- 65% of construction workers routinely work from scaffolds;
- every year, approximately 50 workers are killed and 4,500 are injured in scaffold-related accidents; and
- 72% of scaffold-related injuries were caused by platform failure, support failure, slipping, or being struck by a falling object.
The following inspection tips are derived mainly from the scaffold safety guidelines developed by OSHA, the United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration. Inspectors and construction workers may consult OSHA or their authority having jurisdiction (AHJ) if more specific information is required.
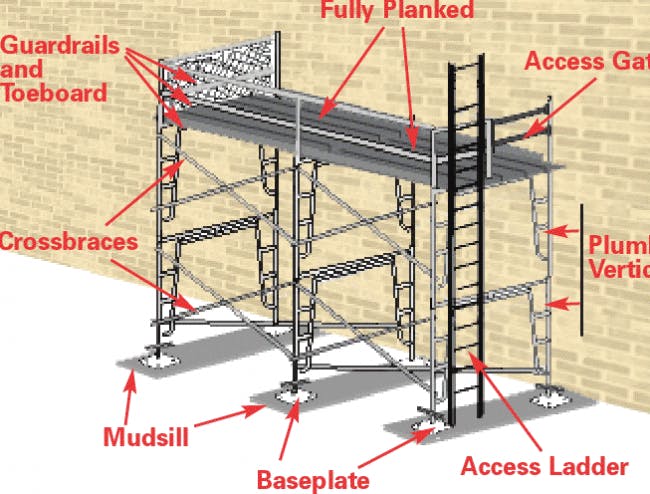
General Scaffold Requirements
- Scaffold components must be able to support at least four times their maximum intended load.
- The scaffolding platform should be fully planked, with no more than a 1-inch gap between planks or planks and uprights.
- The gap between the last plank and the uprights should be less than 9½ inches.
- All platforms should be at least 18 inches wide.
- Guardrail systems or personal fall-arrest systems should be employed where needed.
- The scaffold (minus the guardrail) should be 14 inches or less from the work face, or 18 inches for plastering and lathing.
- Planks should not extend past the ends of the scaffold frames more than 12 inches.
- Casters must be locked before work begins.
- Platform surfaces should be secured and cleated.
- The platform should be free from clutter and any tripping hazards.
- Scaffolding, material and workers must remain at least 10 feet away from power lines.
- The top and bottom plank surfaces should be visible and free from opaque finishes.
- Abutted planks must rest on separate support surfaces.
- Scaffolding components made by different manufacturers must fit together without force.
- A defective scaffold must be removed from service.
Supported Scaffold Requirements
- The height-to-base width ratio should be less than 4:1. Scaffolds that do not meet this requirement must be secured using ties such that the following are true:
- All scaffold frames and uprights should use base plates, and mud sills are required if it is set on dirt.
- Footings should be level, sound and rigid. No settling should have occurred.
- Unstable objects, such as blocks, bricks and buckets, should not be used as work platforms or to support scaffolds.
- Scaffolds should be erected on adequate and firm footings that can support four times the intended load without settling.
- Riggers should be secured and installed correctly.
Scaffold Access
- No more than a 2-foot step up or down or a 14-inch step across should be required to get on or off the platform.
- The first rung of the ladder should not be more than 2 feet above the ground.
- Hook-on and attachable ladders should be of a type designed for use with the scaffold.
- Add-on ladders must have a rung length of at least 11½ inches.
- Built-in ladders that are part of the scaffold frames must have a rung length of at least 8 inches.
- Wooden planks must be free of cracks and splits greater than 1/4-inch.
- Metal components must be free of bends, cracks, holes, rust, welding splatter, pits, broken welds, and non-compatible parts.
- Ladder rungs must line up vertically for the entire height of the scaffold.
- Cross-braces are prohibited for use as a point of access, or for climbing up or down.
- Ladders should be positioned so as to not tip the scaffold.
- Hook-on and attachable ladders must have rung lengths of at least 11½ inches.
- Hook-on and attachable ladders must have uniformly spaced rungs, with a maximum spacing between rungs of 16¾ inches.
- Stairway-type ladders must have slip-resistant treads on all steps and landings.
- Ramps and walkways 6 inches or more above lower levels must have guardrails.
- Ramps and walkways must be inclined with a slope less than 20º above the horizontal.
- Integral, pre-fabricated scaffold access frames should be constructed for use as ladder rungs, and have rung lengths of at least 8 inches.
- Safe access must be provided for all scaffold platforms that are more than 2 feet above or below the point of access.
- Rest platforms must be installed every 35 vertical feet.
Use
- A scaffold and its components must not be loaded beyond their capacity.
- The use of shore or lean-to scaffolds is prohibited.
- Any damaged component must be removed, repaired or replaced.
- Occupied scaffolds must not be moved, unless the scaffold is designed for movement by a professional engineer or is a mobile scaffold.
- The scaffold should not be used in slippery conditions, such as when snow or ice is present, except to remove such hazards.
- Tag lines should be used to control loads being hoisted onto or near scaffolding.
- Tools, material and debris should be removed from the scaffold to prevent accumulation and trip hazards.
- No makeshift devices, such as boxes or barrels, may be used to increase the working-level height.
- No ladders may be placed on the top of the scaffold deck, except under certain large-area scaffolds.
- Provisions need to be made to prevent the platform from deflecting more than 1/60-inch.
Fall Protection
- Some form of personal fall protection is required on all scaffolds higher than 10 feet.
- Fall-arrest systems must be used in high-wind or storm conditions.
- Guardrails must be free of sharp edges.
- Mesh or screens, if equipped, must extend from the top of the guardrail or platform.
- Steel or plastic bands may not be used as railings.
- Requirements regarding falling objects are:
It is good for inspectors to know a little about scaffolding.
###
International Standards of Practice for Inspecting Commercial Properties
